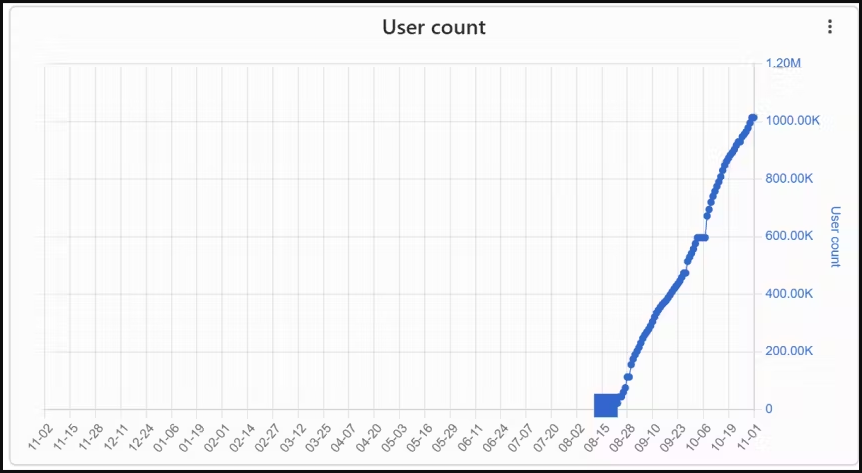
Three malicious Chrome extensions, posing as VPNs, were force-installed 1.5 million times, causing significant concern for users’ security. These extensions, netPlus (1 million installs), netSave, and netWin (500,000 installs), were found to be browser hijackers, cashback hack tools, and data stealers. The malicious extensions were spread via an installer hidden in pirated copies of popular video games and distributed from torrent sites.
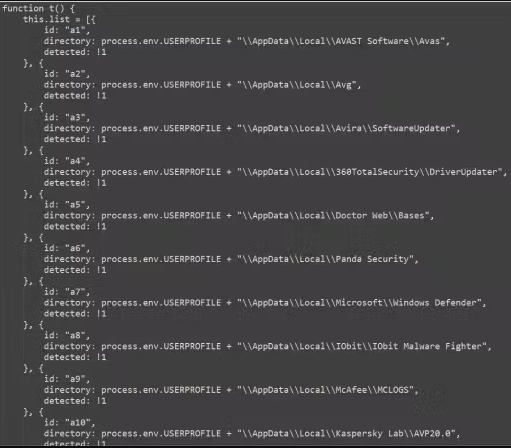
ReasonLabs discovered these malicious extensions and notified Google, leading to their removal from the Chrome Web Store. The campaign appears to target Russian-speaking users, as most infections were in Russia and countries like Ukraine, Kazakhstan, and Belarus. The malicious installer, an electron app measuring between 60MB and 100MB in size, checked for antivirus products on the infected machine and then dropped the malicious extensions on the affected browsers.
The installation of the VPN extensions was automatic and forced, taking place on the registry level, and did not involve the user or require any action on the victim’s side. This type of forced installation is a serious threat to users’ security, as the extensions can potentially steal sensitive data and compromise their online privacy. It is essential for users to be cautious when downloading and installing software, especially from untrusted sources, to avoid falling victim to such malicious campaigns.
Installing fraudulent VPN extensions
ReasonLabs has uncovered a significant security threat involving over a thousand distinct torrent files designed to deliver a malicious installer file. This installer, classified as an electron app and ranging in size from 60MB to 100MB, is responsible for automatically and forcibly installing VPN extensions at the registry level. Interestingly, this installation process requires no user interaction and doesn’t prompt any action from the victim.
Upon successful installation, the malicious installer assesses the infected machine for antivirus products before deploying netSave on Google Chrome and netPlus on Microsoft Edge, ensuring comprehensive coverage across different browsers. To enhance the appearance of legitimacy, the malicious extensions incorporate a realistic VPN user interface featuring some functionality and the option for a paid subscription.
A closer look at the code reveals that the extensions have extensive access to various browser functionalities, including “tabs,” “storage,” “proxy,” “webRequest,” and more. Notably, the ‘offscreen’ permission is exploited, allowing the malware to run scripts through the Offscreen API, clandestinely interacting with the web page’s current Document Object Model (DOM).
This broad access to the DOM equips the extensions with the capability to pilfer sensitive user data, execute browsing hijacks, manipulate web requests, and even disable other extensions installed in the browser. One notable tactic employed by the malware is the deliberate disabling of competing cashback and coupon extensions on the infected device, redirecting profits to the attackers.
ReasonLabs identifies more than 100 targeted cashback extensions, including well-known ones like Avast SafePrice, AVG SafePrice, Honey: Automatic Coupons & Rewards, and others. The communication between the malicious extensions and the command and control (C2) servers involves data exchange related to instructions, commands, victim identification, and the exfiltration of sensitive data.
This report underscores the pervasive security risks associated with web browser extensions, many of which employ obfuscation techniques to conceal their behavior. As a precaution, users are advised to regularly audit their browser extensions, checking for any suspicious activity, and stay informed through reviews in the Chrome Web Store for potential reports of malicious behavior.
Source :
https://cyber.vumetric.com/security-news/2023/12/22/fake-vpn-chrome-extensions-force-installed-1-5-million-times/
https://www.reddit.com/r/cybersecurity/comments/18pmitf/fake_vpn_chrome_extensions_forceinstalled_15/
https://www.reddit.com/r/vpns/comments/18qc203/fake_vpn_chrome_extensions_forceinstalled_15/
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/fake-vpn-chrome-extensions-force-installed-15-million-times/
https://greatis.com/unhackme/help/news/three-malicious-chrome-vpn-extensions-discovered-combining-1-5-million-downloads.htm
https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiJ6UtgD-B46TDbn73whEmidsxY4AZ_CH0WpnFeE48Kn9J053T5l7oCPy0VjDTD4rnFjmyUWL043z0Hb_jcN9Ta6pkOz7mzAQIvAbmMVIxqmalVxfY7RZeuM335PX5Dr229VTfgNR1ERrRlwSHePIWs0b5DMaZUXm027oTEN9Km1W9tQr_f_7ZFyYr_4eMK/s1024/chrome.jpeg