Spirulina, a blue-green microalgae with the Latin name Arthrospira platensis, is recognized for its extraordinary nutritional benefits, with a high protein content of 50% to 70% of its dry weight. In addition to being a rich source of vitamins and minerals, Spirulina also contains bioactive compounds, including carotenoids and antioxidants. Spirulina has been widely developed into food products, cosmetics, and dietary supplements. Given its high potential and demand, Spirulina is now widely cultivated in various countries, including the United States, Thailand, China, India, Taiwan, Pakistan, and Burma. Spirulina cultivation itself can be carried out using several methods. Among the existing methods, these three are popular: open pond systems, photobioreactors, and home cultivation kits that require an integrated artificial intelligence solution with IoT devices.
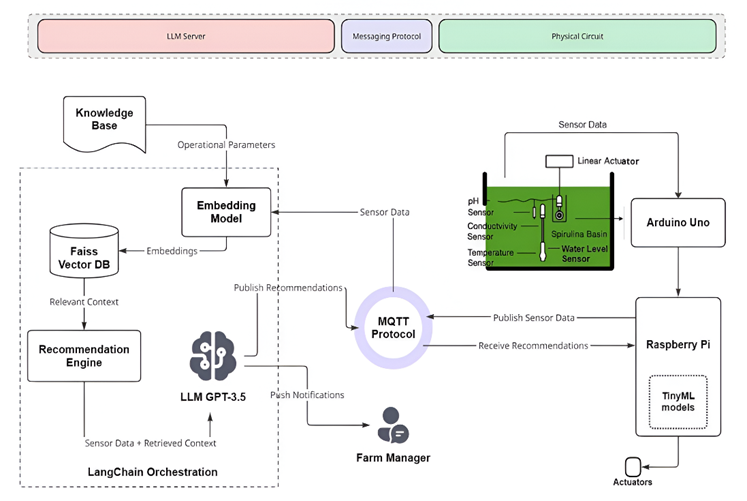
Architecture of the proposed AIoT solution for spirulina cultivation control
In their research, Elbaati et al. (2026) proposed an AIoT system that utilizes Generative AI (such as Large Language Model / LLM) to generate precise recommendations, as well as edge computing (TinyML) to ensure autonomous and stable operations to maintain optimal conditions, automate manual tasks, and substantially increase Spirulina harvest yields and product quality.

The results obtained in this study show that the proposed system (AIoT) can substantially increase the growth rate, biomass yield, and nutritional content of Spirulina. This not only overcomes the limitations of traditional methods but also paves the way for AI-integrated agricultural systems in rural and remote areas, where continuous expert supervision is difficult to obtain.
Read the full article for FREE!
DOI: doi.org/10.11591/ijece.v16i1.pp488-504


